 Beta carotene is a red-orange pigment found in many plants. Its primary use in plants is to protect them from damage by excessive sunlight. Beta carotene also provides many animals with their coloration, especially flamingos, lobsters and other shellfish.
Beta carotene is a red-orange pigment found in many plants. Its primary use in plants is to protect them from damage by excessive sunlight. Beta carotene also provides many animals with their coloration, especially flamingos, lobsters and other shellfish.
The Swiss chemist Paul Karrer and his team deduced the structure of beta-carotene by 1930. It is chemically classified as an isoprenoid, meaning that it is derived from isoprene units. Carotenes are a type of isoprenoid common in carrots that have a chain of eight isoprene units, and beta carotene is so-named because it has a beta ring at each end of this chain.
Carotene is the primary contributor of the red-orange color in many plants, including carrots, cantaloupes, mangoes, papayas, pumpkins and sweet potatoes. Leafy vegetables such as spinach and kale also contain significant levels of beta carotene, although the green color of chlorophyll masks the color of beta carotene in these plants.
The primary nutritional role of carotenes is their conversion to vitamin A, which requires the enzyme 15,15'-monooxygenase. Beta carotene is the best-known provitamin A carotenoid, although members of this class also include alpha carotene and beta cryptoxanthin. Carotenes are soluble in fat, so their absorption increases when they are eaten with fatty foods. Raw vegetables have more carotene, since it is sensitive to heat.
The uses of beta carotene in health supplements generally derives from its role as a vitamin A precursor. These benefits primarily include antioxidant activity, which help support the skin, eyes and lungs.
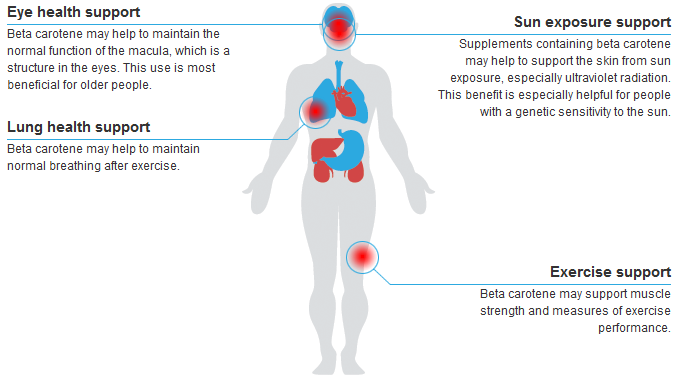
Beta carotene may help to maintain the normal function of the macula, which is a structure in the eyes. This use is most beneficial for older people.
Beta carotene may help to maintain normal breathing after exercise.
Supplements containing beta carotene may help to support the skin from sun exposure, especially ultraviolet radiation. This benefit is especially helpful for people with a genetic sensitivity to the sun.
Beta carotene may support muscle strength and measures of exercise performance.
The most significant indications that you may need beta carotene are the signs of oxidative stress. These signs generally include chronic conditions caused by free radicals, especially skin that’s dry or has an aged appearance. A compromised immune system and poor cardiovascular function are additional signs that you may benefit from beta carotene. Unhealthy blood sugar levels and poor night vision may also mean you need beta carotene.

I also read a book about a skin anti-aging supplement regime. And it is advised to take the below supplements on top of a high-quality multivitamin & fish oil: Acetyl-l-Carnitine (ALC) 2000 mg Folic Acid 800 mcg Thiamine (vit B1) 50 mg ...

Antioxidant Support Carotenoids Background and Benefits Carotenoids are a class of red-orange pigments that are primarily produced by photosynthesizing organisms such as green plants. Some photosynthesizing bacteria and fungi also produce carotenoids, as do spider mites and aphids. The primary bi...
Shipping calculated at checkout